What is a Canonical URL in SEO?

As a website owner, you want to make sure that your content is easily discoverable by search engines and that it’s not being penalized for duplicate content. One way to do this is by using canonical URLs. In this guide, we’ll cover everything you need to know about canonical URLs, including what they are, how they work, and how to implement them on your website.
What is a Canonical URL?
A canonical URL is the preferred URL for a piece of content. It tells search engines which version of the URL you want to be indexed in their search results. This is especially useful for sites that have multiple URLs that point to the same content.
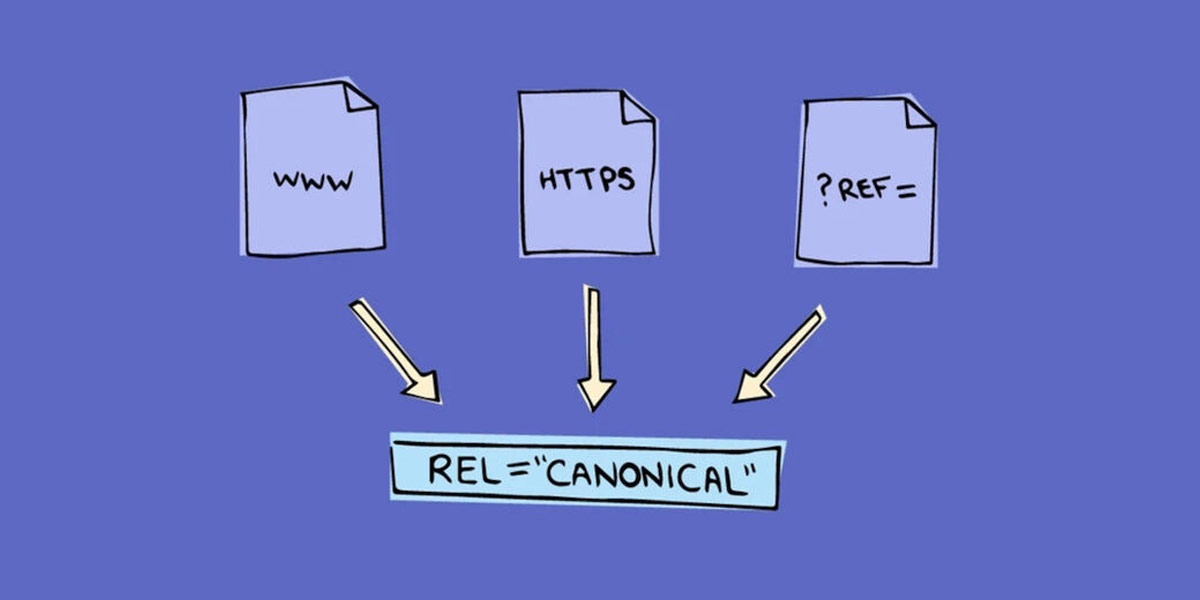
For example, let’s say you have a blog post that can be accessed from multiple URLs:
- https://example.com/blog-post
- https://www.example.com/blog-post
- https://example.com/blog-post?utm_source=facebook&utm_medium=social
All three URLs point to the same content, but search engines may treat them as separate pages, which can lead to duplicate content issues. By specifying a canonical URL, you’re telling search engines that these URLs should be treated as a single page.
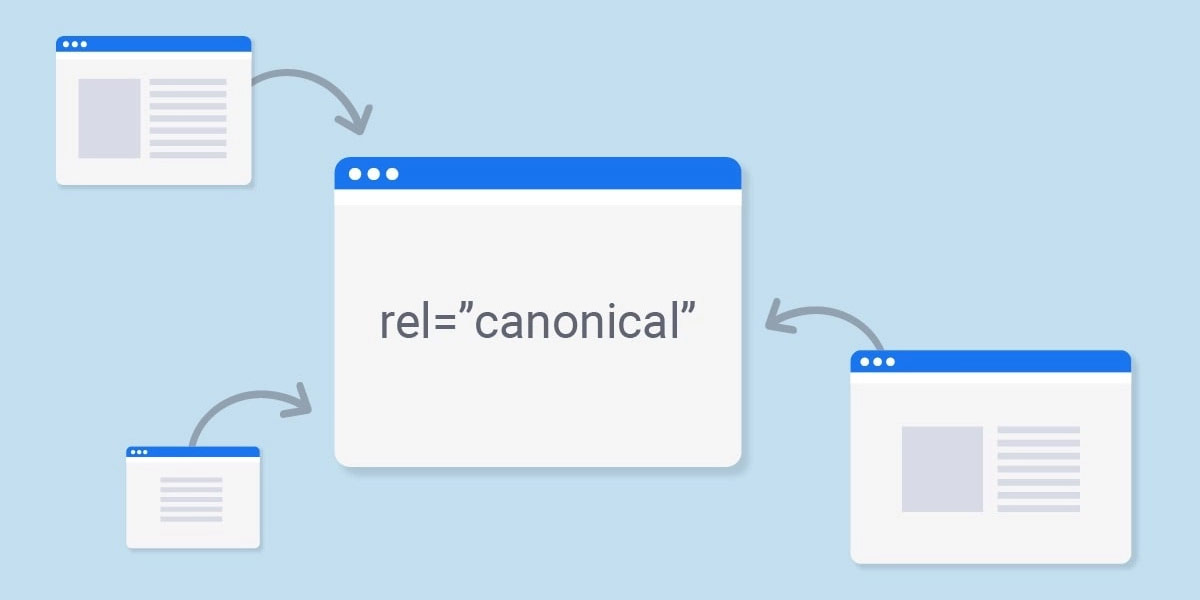
Why are Canonical URLs Important for SEO?
Canonical URLs are important for SEO because they help to avoid duplicate content issues. Duplicate content can confuse search engines and can lead to lower search rankings. By specifying a canonical URL, you’re telling search engines which version of the URL you want to be indexed, which helps to avoid confusion and improve your search rankings.
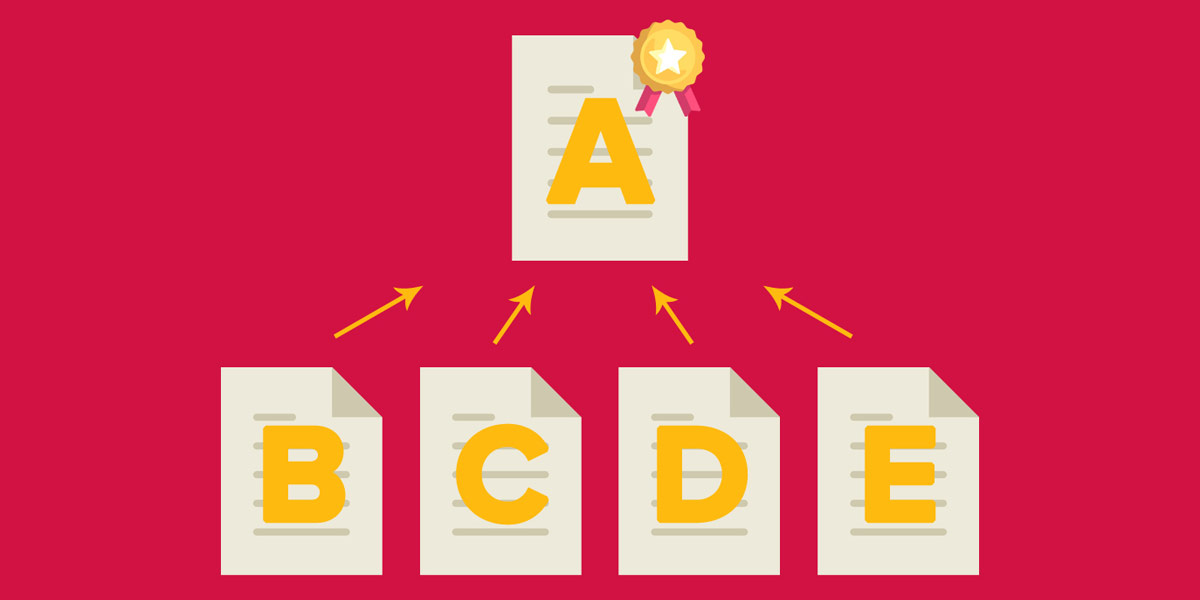
In addition, canonical URLs can help to consolidate link equity. If you have multiple URLs that point to the same content, the link equity for that content may be split between those URLs. By specifying a canonical URL, you’re consolidating all of the link equity for that content to a single URL, which can help to improve the ranking power of that page.
How Do Canonical URLs Work?
Canonical URLs work by specifying a preferred URL for a piece of content. When search engines crawl your site, they will see the canonical tag and understand that this is the preferred URL for that content. This helps to avoid confusion and ensures that the correct version of the URL is indexed.
It’s important to note that canonical URLs don’t redirect users to a different URL. They simply tell search engines which URL to index. Users who access the non-canonical URLs will still be able to view the content, but search engines will only index the canonical URL.
When Should You Use a Canonical URL?
You should use a canonical URL when you have multiple URLs that point to the same content. This can happen for several reasons, such as:
- Your site has both a www and non-www version
- You use tracking parameters in your URLs
- Your site has multiple pages with similar content
By specifying a canonical URL, you’re telling search engines which version of the URL you want to be indexed. This helps to avoid duplicate content issues and ensures that your content is being properly indexed.
How to Implement Canonical URLs on Your Website
There are a few different ways to implement canonical URLs on your website. The most common methods are using canonical tags or setting up redirects
Using Canonical Tags
The easiest way to implement canonical URLs is by using canonical tags. These tags are placed in the head section of your HTML code and tell search engines which URL is the preferred URL for a piece of content. Here’s an example of what a canonical tag looks like:
<link rel="canonical" href="https://example.com/blog-post" />In this example, we’re telling search engines that the preferred URL for our blog post is https://example.com/blog-post.
Setting Up Redirects
Another way to implement canonical URLs is by setting up redirects. This involves redirecting all non-canonical URLs to the canonical URL using a 301 redirect. This tells search engines that the content has permanently moved to a new URL.
For example, if we wanted to redirect all non-canonical URLs for our blog post to the canonical URL, we could set up a 301 redirect like this:
Redirect 301 /blog-post https://example.com/blog-postThis would redirect all non-canonical URLs for our blog post to https://example.com/blog-post.
Best Practices for Implementing Canonical URLs
When implementing canonical URLs, there are a few best practices to keep in mind:
| Best practices for canonical URLs | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Use absolute URLs | Make sure that your canonical URL is an absolute URL that includes the full domain name. |
| Be consistent | Make sure that your canonical URL is consistent across your site. If you change the canonical URL for a piece of content, make sure to update any internal links that point to that content. |
| Use self-referencing canonical tags | For pages that can be accessed from multiple URLs, use a self-referencing canonical tag. This tells search engines that the current URL is the preferred URL for that page. |
Canonical URL vs. 301 Redirects: What’s the Difference?
Canonical URLs and 301 redirects are both ways to consolidate multiple URLs for a piece of content. However, they work in slightly different ways.
A canonical URL tells search engines which URL you want to be indexed, but it doesn’t redirect users to a different URL. Users who access the non-canonical URLs will still be able to view the content, but search engines will only index the canonical URL.
A 301 redirect, on the other hand, redirects users and search engines to a different URL. This tells search engines that the content has permanently moved to a new URL.
In general, you should use canonical URLs when you have multiple URLs that point to the same content but don’t want to redirect users. You should use 301 redirects when you want to permanently redirect users and search engines to a new URL.
Common Canonical URL Mistakes to Avoid
When implementing canonical URLs, there are a few common mistakes that you should avoid:
| Common Mistakes to Avoid | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Using relative URLs | Make sure that your canonical URL is an absolute URL that includes the full domain name. |
| Using the wrong URL | Make sure that your canonical URL is the correct URL for that piece of content. Using the wrong URL can lead to confusion and duplicate content issues. |
| Not updating internal links | If you change the canonical URL for a piece of content, make sure to update any internal links that point to that content. Otherwise, you may end up with multiple URLs that point to the same content. |
Conclusion
Canonical URLs are an important tool for managing duplicate content and consolidating link equity. By specifying a canonical URL for a piece of content, you’re telling search engines which URL you want to be indexed, which helps to avoid confusion and improve your search rankings.
When implementing canonical URLs, it’s important to use absolute URLs, be consistent, and avoid common mistakes like using relative URLs or not updating internal links.
By following these best practices, you can ensure that your content is being properly indexed and that you are getting the most out of your SEO efforts.
FAQs
What is a canonical URL?
A canonical URL is the preferred URL for a piece of content that helps to avoid duplicate content issues and consolidates link equity. It tells search engines which URL to index and can improve your website’s search rankings and visibility.
Why is a canonical URL important for SEO?
A canonical URL is important for SEO because it helps to avoid duplicate content issues and consolidate link equity. When you have multiple URLs that point to the same content, it can confuse search engines and result in lower search rankings. Using a canonical URL ensures that search engines know which URL to index and can help improve your website’s search visibility.
How do I find my canonical URL?
To find your canonical URL, you can use a tool like Google Search Console or a website crawler to identify duplicate content and determine which URL is the preferred one. You can also look for the rel=”canonical” tag in the HTML code of your web pages.
How do I create a canonical URL?
To create a canonical URL, you need to identify the preferred URL for your content and add a rel=”canonical” tag to the HTML code of your web page. The canonical tag should point to the preferred URL, which can be a different URL than the one displayed in the browser’s address bar.
What is the difference between a canonical URL and a redirect?
A canonical URL tells search engines which URL to index for a piece of content, while a redirect tells the browser to send users to a different URL. Canonical URLs are used to avoid duplicate content issues, while redirects are used to permanently or temporarily redirect users to a new URL.
Can canonical URLs be used for internal pages on a website?
Yes, canonical URLs can be used for internal pages on a website. Using canonical URLs for internal pages can help consolidate link equity and avoid duplicate content issues, which can improve your website’s search rankings and visibility.
How do I implement a canonical URL on my website?
To implement a canonical URL on your website, you need to add a rel=”canonical” tag to the HTML code of your web pages. The canonical tag should point to the preferred URL for your content, which can be a different URL than the one displayed in the browser’s address bar.
What are the different ways to specify a canonical URL?
There are a few different ways to specify a canonical URL, including using a rel=”canonical” tag in the HTML code of your web pages, using a 301 redirect, or using the HTTP header field.
What happens if I don’t use canonical URLs?
If you don’t use canonical URLs, you may run into issues with duplicate content, which can confuse search engines and result in lower search rankings. It can also dilute your link equity by having multiple URLs with the same content.
Are canonical URLs necessary for every page on a website?
No, canonical URLs are not necessary for every page on a website. They are primarily used for pages with identical or very similar content to avoid duplicate content issues and consolidate link equity.
How does Google use canonical URLs in search results?
Google uses canonical URLs to determine which URL to index for a piece of content. When there are multiple URLs with the same or very similar content, Google will use the canonical URL to avoid indexing duplicate content.
How do canonical URLs affect duplicate content?
Canonical URLs help to avoid duplicate content issues by telling search engines which URL to index for a piece of content. This can help improve your website’s search rankings and visibility.
Can canonical URLs be used for international versions of a website?
Yes, canonical URLs can be used for international versions of a website. If you have a website with different versions for different languages or regions, you can use canonical tags to indicate which version is the preferred version for search engines to index. This can help to prevent duplicate content issues and ensure that the correct version of your website appears in search results for different regions or languages.
How do canonical URLs affect page rank and link equity?
Canonical URLs can affect page rank and link equity in a few ways. By indicating which version of a page is the preferred version, canonical tags can help to consolidate the link equity and page rank of different versions of the same page. This can help to prevent the dilution of link equity across different versions of the same content and ensure that the preferred version of the page ranks highest in search results. However, it is important to note that canonical URLs do not transfer all link equity to the preferred version of the page. Some link equity may still be distributed across other versions of the page.
What are some common mistakes to avoid when using canonical URLs?
Some common mistakes to avoid when using canonical URLs include:
| Common Mistakes to Avoid When Using Canonical URLs | |
|---|---|
| Using canonical tags incorrectly or inconsistently | Make sure to use canonical tags only when necessary and ensure that they are used consistently across all versions of the page. |
| Using canonical tags for pages with significant content differences | Canonical tags should only be used for pages that have similar or identical content. |
| Using canonical tags for pages that are not part of the same website | Canonical tags should only be used for pages that are part of the same website. |
| Using canonical tags instead of redirects | Canonical tags are not a substitute for redirects and should not be used to redirect users or search engines to a different URL. |

